Back
Clinical: General Topics
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Physical Activity
Friday, March 31, 2023
12:00 PM East Coast USA Time

- CH
Chris Hong, DO
Resident
RowanSOM
Stratford, New Jersey, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background and Hypothesis: COVID-19 disease was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization in March 2020. This was a critical time in our country because obesity has been a national epidemic in the United States. As a result of the dire effects of obesity and the well-known health benefits from physical activity, it is important for us to understand the effects of the pandemic on physical activity in family medicine patients. We hypothesized the COVID-19 pandemic has negatively impacted the family medicine patients from maintaining physical activity as compared to pre-pandemic times.
Methods: Outpatients were recruited in person in the examination rooms at the Rowan Family Medicine clinic located in Washington Township, NJ. Data were collected by hardcopy surveys distributed to the patients after they had consented to participate in the present study. Patients were given hard copies of the questionnaire to complete regarding physical activities and personal demographics.
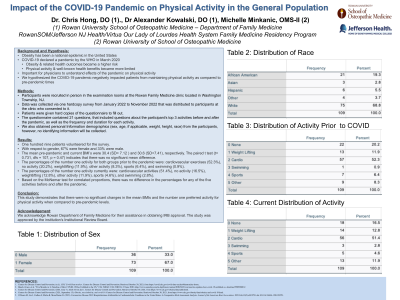
Results: One hundred nine patients volunteered for the survey. With respect to gender, 67% were female and 33% were male. The mean pre-pandemic and current BMI’s were 30.4 (SD= 7.12 ) and 30.6 (SD=7.41), respectively. The paired t test (t= 0.731, dfs = 107, p = 0.47) indicates that there was no significant mean difference. The percentages of the number one activity for both groups prior to the pandemic were: cardiovascular exercises (52.3%), no activity (20.2%), weightlifting (11.9%), other activity (8.3%), sports (6.4%), and swimming (0.9%). The percentages of the number one activity currently were: cardiovascular activities (51.4%), no activity (16.5%), weightlifting (12.8%), other activity (11.9%), sports (4.6%), and swimming (2.8%). Based on the McNemar test for correlated proportions, there was no difference in the percentages for any of the five activities before and after the pandemic.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that there were no significant changes in the mean BMIs and the number one preferred activity for physical activity when compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Acknowledgement of Research Study Sponsors and IRB: We acknowledge Rowan Department of Family Medicine for their assistance in obtaining IRB approval. The study was approved by the institution’s Institutional Review Board.
Methods: Outpatients were recruited in person in the examination rooms at the Rowan Family Medicine clinic located in Washington Township, NJ. Data were collected by hardcopy surveys distributed to the patients after they had consented to participate in the present study. Patients were given hard copies of the questionnaire to complete regarding physical activities and personal demographics.
Results: One hundred nine patients volunteered for the survey. With respect to gender, 67% were female and 33% were male. The mean pre-pandemic and current BMI’s were 30.4 (SD= 7.12 ) and 30.6 (SD=7.41), respectively. The paired t test (t= 0.731, dfs = 107, p = 0.47) indicates that there was no significant mean difference. The percentages of the number one activity for both groups prior to the pandemic were: cardiovascular exercises (52.3%), no activity (20.2%), weightlifting (11.9%), other activity (8.3%), sports (6.4%), and swimming (0.9%). The percentages of the number one activity currently were: cardiovascular activities (51.4%), no activity (16.5%), weightlifting (12.8%), other activity (11.9%), sports (4.6%), and swimming (2.8%). Based on the McNemar test for correlated proportions, there was no difference in the percentages for any of the five activities before and after the pandemic.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that there were no significant changes in the mean BMIs and the number one preferred activity for physical activity when compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Acknowledgement of Research Study Sponsors and IRB: We acknowledge Rowan Department of Family Medicine for their assistance in obtaining IRB approval. The study was approved by the institution’s Institutional Review Board.
